Objective: To evaluate the clinical outcomes of two different rotational space preparation techniques for the extraction of bilateral impacted mandibular supernumerary teeth with curved root in a single patient.
Diagnosis and treatment: The patient was a 23-year-old female. Initial eruption of supernumerary cusps was observed on the lingual side of teeth
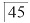
. On the lingual side of
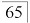
, the mucosa appeared pale, and bony bulging caused by the right supernumerary tooth was palpable. Preoperative cone beam computed tomography(CBCT) revealed that the bilateral mandibular supernumerary teeth resembled premolars in morphology and exhibited pronounced root curvature. The left supernumerary tooth was located near the alveolar crest, whereas the right one was positioned below the alveolar crest. Based on the different impaction conditions, odontotomy and ostectomy were employed respectively to prepare rotational space for the extraction of the curved-root supernumerary teeth.
Results: Both impacted curved-root supernumerary teeth were successfully and easily extracted. Postoperative healing was uneventful, with no abnormalities in adjacent teeth and no evidence of lower lip numbness. CBCT performed six months postoperatively demonstrated satisfactory bone regeneration at the extraction sockets.
Conclusions: Both rotational space preparation techniques provide efficient resistance elimination during the extraction of impacted curved-root supernumerary teeth and ensure a low incidence of complications, including inferior alveolar nerve injury and adjacent tooth trauma.
